How to Become a Medical Illustrator
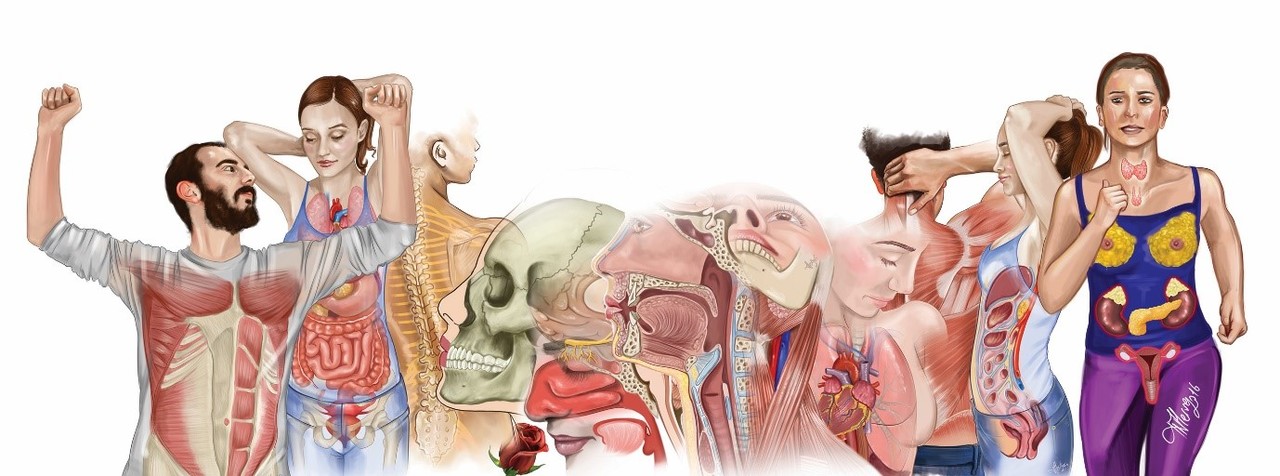
Learn how to become a medical illustrator and combine your passion for art with scientific expertise
How to Become a Medical Illustrator
In the world of healthcare and scientific communication, the role of a medical illustrator is both unique and vital. Medical illustrators are the creative minds behind the visually captivating representations of complex medical and scientific information. If you have a passion for art, a keen eye for detail, and an interest in the medical field, then becoming a medical illustrator might be the perfect career path for you. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the steps and requirements to become a successful medical illustrator.
What does a Medical Illustrator do?
Medical illustrators are professionals who specialize in translating complex medical and scientific concepts into visual and easily understandable forms. They create illustrations, animations, and graphics that are used in medical textbooks, research papers, educational materials, surgical procedures, and even patient education. Their work is crucial for enhancing the comprehension of medical information among students, healthcare professionals, and the general public.
Qualification Required to Become a Medical Illustrator
To embark on a career as a medical illustrator, you'll need a strong educational foundation. Typically, a bachelor's degree in a related field is the first step. Majors such as biology, anatomy, or fine arts are excellent choices. However, many aspiring medical illustrators opt for specialized programs specifically designed for this profession. These programs provide a blend of scientific knowledge and artistic skills necessary for success in this field.
Types of Medical Illustrator
Medical illustration is a diverse field, and professionals can specialize in various areas, including:
1. Anatomical Illustrator
Anatomical illustrators are experts in the intricacies of human and animal anatomy. They create detailed and accurate illustrations of organs, tissues, bones, and other anatomical structures. These illustrations are often used in medical textbooks, surgical guides, and educational materials to help students, healthcare professionals, and researchers understand the human body's complexity.
2. Surgical Illustrator
Surgical illustrators focus on creating visuals that are essential for surgical procedures. Their illustrations assist surgeons in pre-operative planning, providing them with a visual roadmap of the surgery. These visuals can include detailed depictions of surgical techniques, instrument usage, and step-by-step guides for specific procedures. Surgical illustrators play a critical role in enhancing surgical precision and safety.
3. Biomedical Animator
Biomedical animators use animation and multimedia techniques to bring complex biological processes to life. They create dynamic visuals that explain intricate cellular processes, molecular interactions, and the functioning of biological systems. Biomedical animations are valuable for educational purposes, medical research, and patient education, as they simplify challenging concepts and make them accessible to a broad audience.
4. Veterinary Illustrator
Veterinary illustrators specialize in the illustration of animals and their anatomy. Their work is primarily used in veterinary education, research publications, and veterinary clinics. Veterinary illustrators create visual materials that aid veterinarians in diagnosing and treating animals. They may illustrate animal anatomy, medical procedures, and disease pathology specific to animals.
5. Medical Legal Illustrator
Medical legal illustrators combine their artistic skills with a deep understanding of medical and legal terminology. They create visual exhibits and illustrations for use in legal proceedings, particularly in medical malpractice and personal injury cases. These illustrations help lawyers, judges, and jurors comprehend complex medical issues and evidence, making them a crucial part of the legal system.
6. Scientific Illustrator
While not exclusive to the medical field, scientific illustrators create visuals that communicate scientific concepts across various disciplines, including biology, chemistry, and geology. In the medical context, they may create illustrations for research papers, scientific journals, and educational materials. Scientific illustrators have a broad skill set and can adapt their work to different scientific subjects.
7. 3D Medical Modeler
With advancements in technology, 3D medical modelers have gained prominence. They specialize in creating three-dimensional models of anatomical structures, organs, or medical devices. These models are used for educational purposes, surgical planning, and medical device development. 3D medical modelers work with software and physical prototypes to bring precision and depth to medical visuals.
These specialized types of medical illustrators contribute significantly to the healthcare and scientific communities by translating complex information into visually engaging and comprehensible formats. Depending on your interests and skills, you can choose the path that aligns best with your passion for art and science within the field of medical illustration.
Medical Illustrator Degrees and Requirements
While a bachelor's degree is essential, many medical illustrators pursue master's degrees to gain a more specialized education. A Master of Science in Medical Illustration (MSMI) is highly regarded in the field. These programs delve deeper into the science and artistry required for medical illustration.
In addition to formal education, aspiring medical illustrators should develop strong digital illustration and 3D modeling skills. Proficiency in software tools such as Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and 3D modeling software is crucial.
How Long Does it take to Become a Medical Illustrator
The duration to become a medical illustrator can vary. A bachelor's degree typically takes four years to complete. If you choose to pursue a master's degree, it will add another two to three years to your educational journey. After completing your education, gaining experience through internships or entry-level positions is essential.
Pros & Cons of Becoming a Medical Illustrator
Pros:
- Fulfilling Career: You'll have the satisfaction of contributing to medical education and research.
- Creative Outlet: The profession allows you to merge your passion for art with science.
- Job Stability: The demand for medical illustrators remains steady.
Cons:
- Extensive Education: It requires several years of education and training.
- Competitive Field: The field is highly competitive, and landing your first job can be challenging.
- Detail-Oriented: Attention to detail is critical, which can be mentally exhausting.
Tips for Getting a Work as a Medical Illustrator
Build a Strong Portfolio: Showcase your best work in a portfolio that demonstrates your skills and style.
Networking: Attend conferences, join professional organizations, and connect with professionals in the field.
Stay Updated: Keep up with advancements in both medicine and illustration techniques.
Internships: Seek internships or freelance opportunities to gain practical experience.
Diversify Your Skills: Learn different illustration styles and explore 3D modeling and animation.
In conclusion, becoming a medical illustrator is a challenging yet rewarding journey for those with a passion for both art and science. It requires dedication, continuous learning, and perseverance. However, the opportunity to contribute to the medical field through your creative talents is immensely fulfilling.
FAQs
1. Is a master's degree necessary to become a medical illustrator?
A master's degree is not always necessary to become a medical illustrator, but it can be highly beneficial for your career. The path to becoming a medical illustrator offers some flexibility in terms of educational requirements, and the choice between a bachelor's degree or a master's degree depends on your goals and circumstances.
Here's a breakdown of the educational options for aspiring medical illustrators:
Bachelor's Degree: Many medical illustrators start with a bachelor's degree in a related field, such as biology, anatomy, fine arts, or a combination of these disciplines. This foundational education provides a strong background in science and art, which are essential for the profession. A bachelor's degree typically takes four years to complete.
Master's Degree: While a master's degree is not mandatory, it can offer several advantages. A Master of Science in Medical Illustration (MSMI) is a specialized program that provides in-depth training in both scientific and artistic aspects of medical illustration. These programs often include courses in anatomy, physiology, pathology, and advanced illustration techniques. A master's degree can enhance your skills and knowledge, making you more competitive in the field. These programs typically take an additional two to three years to complete.
Certification Programs: In addition to bachelor's and master's degrees, there are also certification programs and workshops available in medical illustration. These shorter programs can be a good option for individuals looking to develop specific skills or enhance their portfolio. However, they may not provide the same level of comprehensive training as a degree program.
Ultimately, the decision regarding your level of education should align with your career goals and personal circumstances. Some medical illustrators have successfully entered the field with a bachelor's degree and a strong portfolio, while others have pursued master's degrees to gain a more specialized education.
Regardless of your educational path, building a strong portfolio that showcases your skills and demonstrates your ability to create accurate and engaging medical illustrations is crucial for success in this field. Additionally, ongoing professional development, networking, and staying up-to-date with advancements in both medicine and illustration techniques will play a significant role in your career as a medical illustrator.
2. What are the job prospects for medical illustrators?
Job prospects can vary, but medical illustrators are generally in demand in healthcare, publishing, and research sectors. Networking and a strong portfolio can improve your chances of finding work.
3. Are there opportunities for freelance medical illustrators?
Yes, many medical illustrators work as freelancers, taking on projects for various clients, including healthcare institutions and educational publishers.
4. What software tools do medical illustrators commonly use?
Medical illustrators often use software like Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and 3D modeling software to create their illustrations and animations.
5. How can I start building my portfolio as a prospective medical illustrator?
Start by creating illustrations related to anatomy and biology. You can also collaborate with educators or researchers on visual projects to build your portfolio.
- Share This Job



Write A Comment
No Comments